TensorFlow笔记1-2-图片数据建模流程范例
一、准备数据
cifar2数据集为cifar10数据集的子集,只包括前两种类别airplane和automobile。
训练集有airplane和automobile图片各5000张,测试集有airplane和automobile图片各1000张。
cifar2任务的目标是训练一个模型来对飞机airplane和机动车automobile两种图片进行分类。
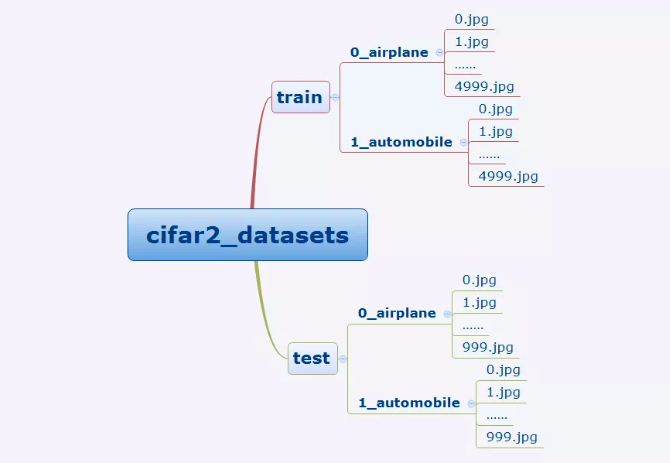
我们准备的Cifar2数据集的文件结构如下所示。
方案有两种,第一种是使用tf.keras中的ImageDataGenerator工具构建图片数据生成器。
第二种是使用tf.data.Dataset搭配tf.image中的一些图片处理方法构建数据管道。
第一种方法更为简单,其使用范例可以参考以下文章。
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/67466552
第二种方法是TensorFlow的原生方法,更加灵活,使用得当的话也可以获得更好的性能。
我们此处介绍第二种方法。
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import datasets,layers,models
BATCH_SIZE = 100
def load_image(img_path,size = (32,32)):
label = tf.constant(1,tf.int8) if tf.strings.regex_full_match(img_path,".*automobile.*") \
else tf.constant(0,tf.int8) # 图片名匹配label=1,否则为0
img = tf.io.read_file(img_path)
img = tf.image.decode_jpeg(img) #注意此处为jpeg格式
img = tf.image.resize(img,size)/255.0
return(img,label)
#使用并行化预处理num_parallel_calls 和预存数据prefetch来提升性能
ds_train = tf.data.Dataset.list_files("./data/cifar2/train/*/*.jpg") \
.map(load_image, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE) \
.shuffle(buffer_size = 1000).batch(BATCH_SIZE) \
.prefetch(tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)
ds_test = tf.data.Dataset.list_files("./data/cifar2/test/*/*.jpg") \
.map(load_image, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE) \
.batch(BATCH_SIZE) \
.prefetch(tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)
%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'svg'
#查看部分样本
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(4,4))
for i,(img,label) in enumerate(ds_train.unbatch().take(9)):
ax=plt.subplot(3,3,i+1)
ax.imshow(img.numpy())
ax.set_title("label = %d"%label)
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
plt.show()
for x,y in ds_train.take(1):
print(x.shape,y.shape)
二、定义模型
使用Keras接口有以下3种方式构建模型:
- 使用Sequential按层顺序构建模型
- 使用函数式API构建任意结构模型
- 继承Model基类构建自定义模型
此处选择使用函数式API构建模型。
tf.keras.backend.clear_session() #清空会话
inputs = layers.Input(shape=(32,32,3))
x = layers.Conv2D(32,kernel_size=(3,3))(inputs)
x = layers.MaxPool2D()(x)
x = layers.Conv2D(64,kernel_size=(5,5))(x)
x = layers.MaxPool2D()(x)
x = layers.Dropout(rate=0.1)(x)
x = layers.Flatten()(x)
x = layers.Dense(32,activation='relu')(x)
outputs = layers.Dense(1,activation = 'sigmoid')(x)
model = models.Model(inputs = inputs,outputs = outputs)
model.summary()
三、训练模型
训练模型通常有3种方法,内置fit方法,内置train_on_batch方法,以及自定义训练循环。此处我们选择最常用也最简单的内置fit方法。
import datetime
import os
stamp = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S")
logdir = os.path.join('data', 'autograph', stamp)
## 在 Python3 下建议使用 pathlib 修正各操作系统的路径
# from pathlib import Path
# stamp = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S")
# logdir = str(Path('./data/autograph/' + stamp))
tensorboard_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.TensorBoard(logdir, histogram_freq=1)
model.compile(
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
loss=tf.keras.losses.binary_crossentropy,
metrics=["accuracy"]
)
history = model.fit(ds_train,epochs= 10,validation_data=ds_test,
callbacks = [tensorboard_callback],workers = 4)
四、评估模型
%load_ext tensorboard
#%tensorboard --logdir ./data/keras_model
from tensorboard import notebook
notebook.list()
#在tensorboard中查看模型
notebook.start("--logdir ./data/autograph")
import pandas as pd
dfhistory = pd.DataFrame(history.history)
dfhistory.index = range(1,len(dfhistory) + 1)
dfhistory.index.name = 'epoch'
dfhistory
%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'svg'
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_metric(history, metric):
train_metrics = history.history[metric]
val_metrics = history.history['val_'+metric]
epochs = range(1, len(train_metrics) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, train_metrics, 'bo--')
plt.plot(epochs, val_metrics, 'ro-')
plt.title('Training and validation '+ metric)
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel(metric)
plt.legend(["train_"+metric, 'val_'+metric])
plt.show()
plot_metric(history,"loss")
plot_metric(history,"accuracy")
#可以使用evaluate对数据进行评估
val_loss,val_accuracy = model.evaluate(ds_test,workers=4)
print(val_loss,val_accuracy)
五、使用模型
可以使用model.predict(ds_test)进行预测。
也可以使用model.predict_on_batch(x_test)对一个批量进行预测。
model.predict(ds_test)
for x,y in ds_test.take(1):
print(model.predict_on_batch(x[0:20]))
六、保存模型
推荐使用TensorFlow原生方式保存模型。
# 保存权重,该方式仅仅保存权重张量
model.save_weights('./data/tf_model_weights.ckpt',save_format = "tf")
# 保存模型结构与模型参数到文件,该方式保存的模型具有跨平台性便于部署
model.save('./data/tf_model_savedmodel', save_format="tf")
print('export saved model.')
model_loaded = tf.keras.models.load_model('./data/tf_model_savedmodel')
model_loaded.evaluate(ds_test)
评论


